A Precarious Recovery: Food Security Remains Uncertain in the Horn of Africa
Although a repeat famine is unlikely, the situation in East Africa remains dire despite recent rains.
By Codi Yeager
Circle of Blue
Increased rainfall has reinforced some East African croplands — for now — and a drop in cereal prices has also helped, but these gains remain fragile, experts say. Many communities in the Horn of Africa are still struggling to recover from last year’s devastating drought and famine, and they continue to face water and food deficits this year.
“More than 9 million people still remain in need of emergency assistance, and conditions may deteriorate further as the major rains and harvest are forecast to be below average,” a United States Agency for International Development (USAID) spokesperson wrote in a statement to Circle of Blue. “The United States continues to be deeply concerned.”
–USAID Spokesperson
Food security in the region is largely dependent on seasonal rains, which in recent years have failed at worst and performed inconsistently at best.
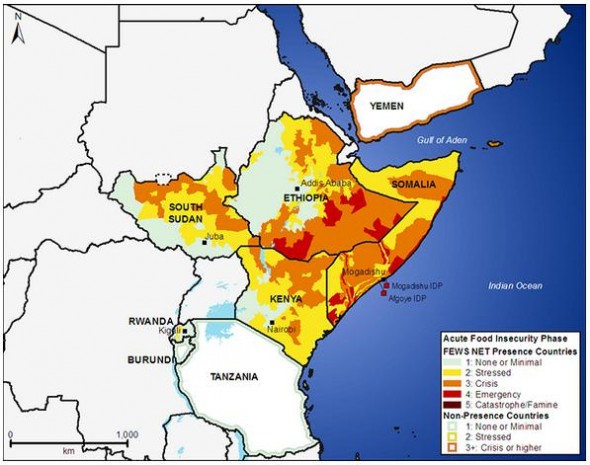
For example, rains from June through September have decreased approximately 15 percent to 20 percent over the past 20 years in southern Ethiopia, according to an analysis by USAID’s Famine Early Warning Systems Network (FEWS NET). Furthermore, precipitation across the Horn during last year’s main rainy season, from April through June, amounted to only 30 percent of the 15-year average (from 1995-2010) in some areas, according to data compiled by the United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA) and FEWS NET.
2011 Crisis / 2012 Reprieve
Poor performances like this led to the Horn’s worst drought in 50 years, which last year withered crops, killed livestock, and pushed up food prices — conditions that eventually led to the widespread food crisis. By the end of July 2011, the United Nations had declared famine in parts of Somalia, which was further aggravated by political instability that blocked the delivery of aid.
Above-average rains from October through November of last year helped restore crop production and pastoral conditions, USAID’s spokesperson wrote to Circle of Blue. In Somalia, the resulting harvest decreased the number of people needing life-saving aid from 4 million to 2.3 million, and the United Nations then declared the famine to be over, OCHA reported in February.
But the report also warned that food stocks from that harvest could run low by May.
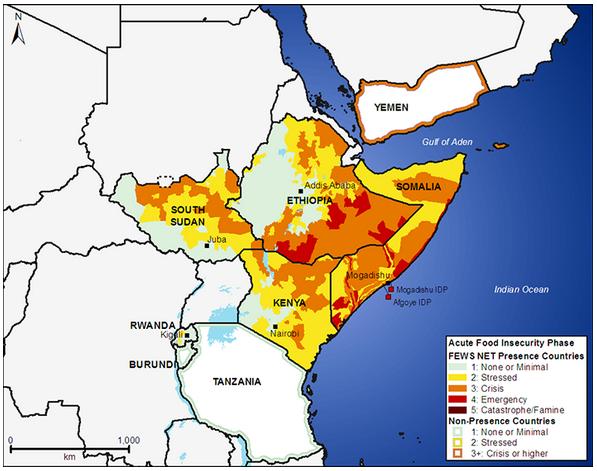
This year’s primary rains — beginning in April — have, so far, been uneven in distribution and timing. Northern and central Somalia have received only delayed and erratic rains, but pasture and water conditions are now average or above-average in most areas of southern Somalia, according to USAID. Water supplies have also been replenished in pastoral and agro-pastoral areas of Ethiopia’s Somali Region, parts of southern Tigray Region, and in the North Wollo, South Wollo, and Oromiya zones of Amhara Region.
It is unclear how long these advances will last, however.
“Crops fed by these rains are reported to face serious risks, due to the forecasted cessation of the rains resulting in a shortened growing period,” USAID’s spokesperson wrote. “Acute water shortages are already present in southwestern regions of Ethiopia, impacting water availability for people, their livestock, and crop production. For example, the sweet potato crop that typically helps smallholder families through the hunger season is expected to be severely reduced, creating food deficits early in the year.”
–USAID Spokesperson
International Aid
In March, the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) appealed for $US 50 million to strengthen the Horn of Africa’s resilience to drought, saying that continued international aid is key to avoiding another crisis.
Overall, aid agencies have requested $US 2.78 billion for the Horn, but only 24.1 percent has been funded, according to OCHA’s most recent Humanitarian Bulletin. USAID committed $US 120 million last week, bringing its total contributions to $US 1.1 billion since the onset of the 2011 crisis.
“This assistance is targeted to avoid the crisis from escalating in Ethiopia, Kenya, and Somalia where the lateness and insufficiency of rains are expected to have a significant negative impact on crop production,” USAID’s spokesperson wrote to Circle of Blue.
The combination of international aid, improved rains, and lower food prices mean it is unlikely that the Horn of Africa will experience a repeat of last year’s famine, according to USAID.
“The situation continues to be serious, but forecasts at this point do not indicate a food crisis of the same severity as in 2011.”
A news correspondent for Circle of Blue based out of Hawaii. She writes The Stream, Circle of Blue’s daily digest of international water news trends. Her interests include food security, ecology and the Great Lakes.
Contact Codi Kozacek









Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!