The United States produces 1 billion tons of coal a year, most of it burned in the nation’s 600 coal-fired utilitiies. In the competition between energy and water, coal is in a league by itself. Roughly half of the 410 billion gallons of water withdrawn every day from the nation’s rivers, lakes, and aquifers is used to mine coal, and cool electric power generating stations, most of which burn coal.
The Department of Energy forecasts that energy demand in the U.S. will grow 40 percent in the next four decades, and much of that growth will occur in the fast-growing southwest, Rocky Mountain region, and southeast, where climate change is reducing rainfall and snowmelt. Where coal falls in the nation’s energy picture will be decided, in large part, by the industry’s access to fresh water.
Coal, though, also is the largest source of climate-changing emissions of any industrial sector, as well as a significant source of water pollution. Evidence of the unholy water and coal alliance is visible along Virginia’s Clinch River and one of its tributaries, Dumps Creek. In the last half-century, three toxic spills have contaminated the Clinch. But it’s not unusual for state regulatory agencies to turn a blind eye when coal companies violate the Clean Water Act. In 2009, a New York Times investigation found that state agencies nationwide have taken action against fewer than three percent of Clean Water Act violators.
 https://www.circleofblue.org/wp-content/uploads/2008/11/Screen-Shot-2016-01-05-at-2.13.05-PM.png
345
586
Brett Walton
https://www.circleofblue.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Circle-of-Blue-Water-Speaks-600x139.png
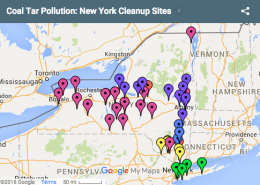
Brett Walton2011-01-17 09:39:392016-01-05 14:19:35Water Pollution Solution — New York Experiments with Coal Tar “Sponges” in Hudson River
https://www.circleofblue.org/wp-content/uploads/2008/11/Screen-Shot-2016-01-05-at-2.13.05-PM.png
345
586
Brett Walton
https://www.circleofblue.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Circle-of-Blue-Water-Speaks-600x139.png
Brett Walton2011-01-17 09:39:392016-01-05 14:19:35Water Pollution Solution — New York Experiments with Coal Tar “Sponges” in Hudson River